Teleradiology and Its Impact on Rural Healthcare Delivery
Updated on: 29 April, 2025
In today’s digital world, technology has transformed every aspect of life — from how we shop for groceries to how we manage our health. Healthcare has embraced this digital revolution too, moving beyond simple fitness trackers to delivering advanced medical services remotely.
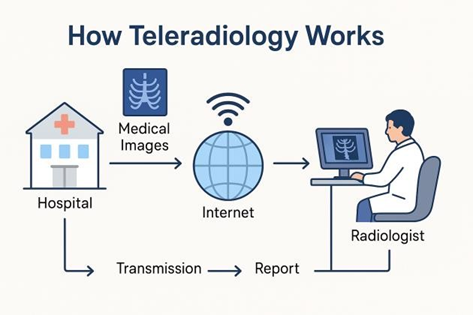
One of the most important advancements in healthcare technology is teleradiology. It has played a major role in bridging the gap between rural and urban healthcare facilities. In simple terms, teleradiology refers to the transmission of medical images — like CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays — from one location to another, where a radiologist can review and report them without being physically present.
For patients living in rural areas or smaller towns, accessing specialist care has always been challenging. Many times, they had to travel long distances to bigger cities just to get imaging reports, leading to delays in diagnosis, extra travel expenses, and unnecessary stress. Teleradiology has changed this scenario dramatically, enabling faster and easier access to specialist opinions without the need for travel.
Also Read: Teleradiology and Its Impact on Rural Healthcare Delivery
With the help of improved internet connectivity and secure digital platforms, medical images can now be shared seamlessly with radiologists across the globe. Hospitals typically use PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) to store medical images, while DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standards ensure these images can be shared and viewed correctly. Together, these systems make it possible for a radiologist to access images, analyze them, and deliver reports in just a few hours — no matter where they are located.
The importance of teleradiology becomes even more evident in emergency cases like trauma, strokes, or internal bleeding, where timely diagnosis can be life-saving. Quick reporting improves treatment decisions and, ultimately, patient outcomes.
Another major advantage of teleradiology is cost-effectiveness. Setting up a full-fledged radiology department with in-house radiologists can be expensive, especially for small hospitals and diagnostic centers. With teleradiology, a single radiologist can provide reporting services to multiple centers, significantly reducing costs without compromising on quality.
Challenges in Teleradiology
Despite its many advantages, teleradiology faces certain challenges:
- Internet Connectivity: Reliable and high-speed internet is critical, yet many rural areas still struggle with weak networks.
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting patient data during transmission is crucial, and not all healthcare workers are fully trained to manage digital systems securely.
- Training and Adaptation: Staff must be comfortable using digital tools to ensure smooth workflow and minimize errors.
Fortunately, with continuous digital development and government initiatives aimed at improving rural internet access and cybersecurity, these challenges are steadily being addressed.
Conclusion
Teleradiology is truly a game-changer for healthcare delivery in rural areas. It provides faster diagnosis, quicker access to specialists, and helps bridge the healthcare gap between rural and urban populations.
With growing investment in healthcare technology, the future of teleradiology looks even brighter. Hospitals and diagnostic centers should focus on building strong teleradiology networks, training staff, and ensuring the highest standards of data security.
By doing so, we move closer to a future where quality healthcare is accessible to everyone, regardless of where they live.
SHIVAM BHARDWAJ
Assistant Professor
Department of Radio-Imaging Technology
Faculty of Allied Health Sciences
SGT University

